Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
Editorials & Other Articles
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
How Europe became so rich

In a time of great powers and empires, just one region of the world experienced extraordinary economic growth. How?
https://aeon.co/essays/how-did-europe-become-the-richest-part-of-the-world

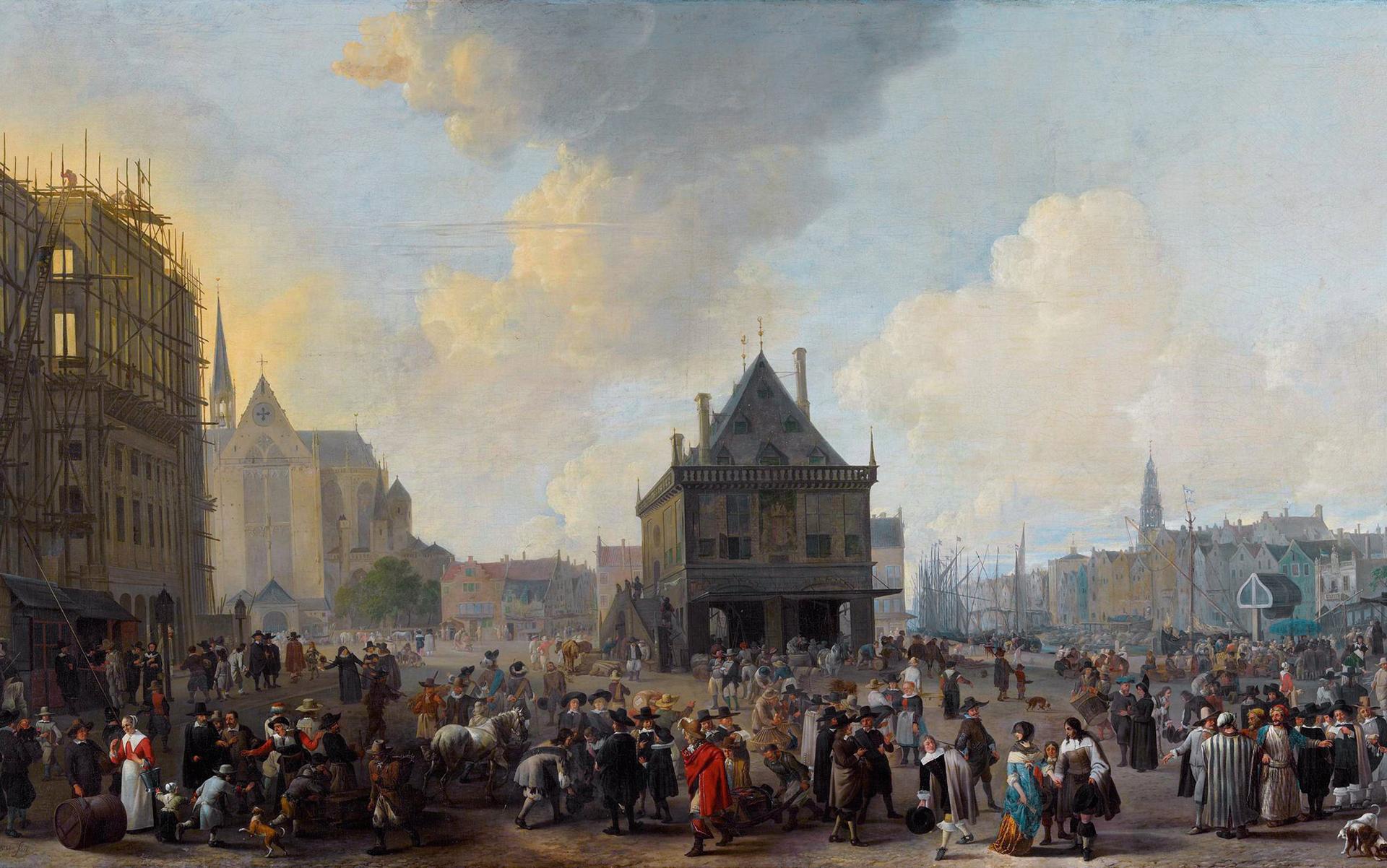
Dam Square with the New Town Hall under Construction (1656) by Johannes Lingelbach. Photo courtesy The Amsterdam Museum/Wikipedia

How and why did the modern world and its unprecedented prosperity begin? Learned tomes by historians, economists, political scientists and other scholars fill many bookshelves with explanations of how and why the process of modern economic growth or ‘the Great Enrichment’ exploded in western Europe in the 18th century. One of the oldest and most persuasive explanations is the long political fragmentation of Europe. For centuries, no ruler had ever been able to unite Europe the way the Mongols and the Mings had united China. It should be emphasised that Europe’s success was not the result of any inherent superiority of European (much less Christian) culture. It was rather what is known as a classical emergent property, a complex and unintended outcome of simpler interactions on the whole.
The modern European economic miracle was the result of contingent institutional outcomes. It was neither designed nor planned. But it happened, and once it began, it generated a self-reinforcing dynamic of economic progress that made knowledge-driven growth both possible and sustainable. How did this work? In brief, Europe’s political fragmentation spurred productive competition. It meant that European rulers found themselves competing for the best and most productive intellectuals and artisans. The economic historian Eric L Jones called this ‘the States system’. The costs of European political division into multiple competing states were substantial: they included almost incessant warfare, protectionism, and other coordination failures. Many scholars now believe, however, that in the long run the benefits of competing states might have been larger than the costs. In particular, the existence of multiple competing states encouraged scientific and technological innovation.
The idea that European political fragmentation, despite its evident costs, also brought great benefits, enjoys a distinguished lineage. In the closing chapter of The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire (1789), Edward Gibbon wrote: ‘Europe is now divided into 12 powerful, though unequal, kingdoms.’ Three of them he called ‘respectable commonwealths’, the rest ‘a variety of smaller, though independent, states’. The ‘abuses of tyranny are restrained by the mutual influence of fear and shame’, Gibbon wrote, adding that ‘republics have acquired order and stability; monarchies have imbibed the principles of freedom, or, at least, of moderation; and some sense of honour and justice is introduced into the most defective constitutions by the general manners of the times.’
In other words, the rivalries between the states, and their examples to one another, also meliorated some of the worst possibilities of political authoritarianism. Gibbon added that ‘in peace, the progress of knowledge and industry is accelerated by the emulation of so many active rivals’. Other Enlightenment writers, David Hume and Immanuel Kant for example, saw it the same way. From the early 18th-century reforms of Russia’s Peter the Great, to the United States’ panicked technological mobilisation in response to the Soviet Union’s 1957 launch of Sputnik, interstate competition was a powerful economic mover. More important, perhaps, the ‘states system’ constrained the ability of political and religious authorities to control intellectual innovation. If conservative rulers clamped down on heretical and subversive (that is, original and creative) thought, their smartest citizens would just go elsewhere (as many of them, indeed, did).
snip